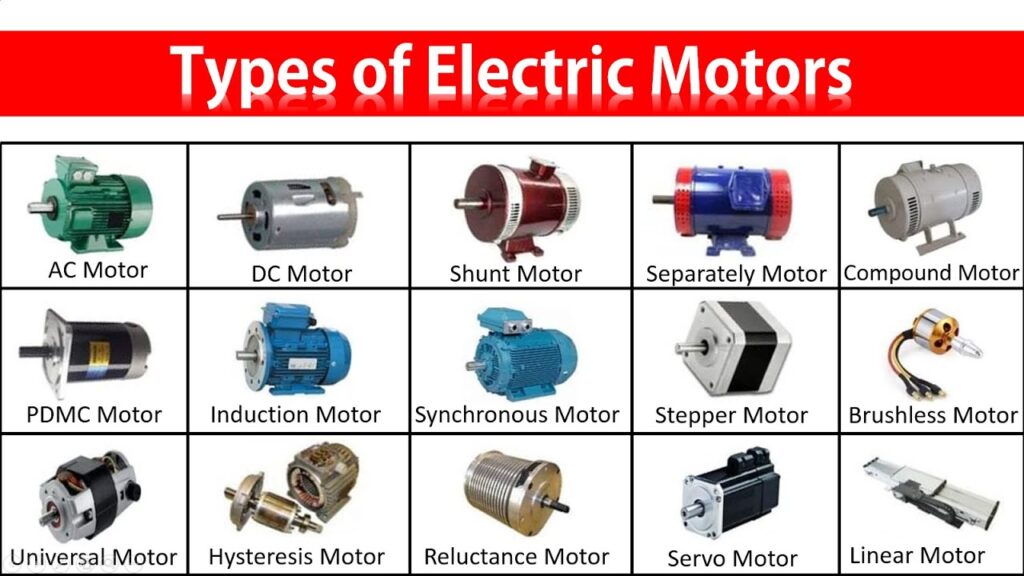
Introduction to Motor Types
Motors are the unsung heroes of technology, powering everything from household appliances to industrial machines. With a diverse range of types available, each motor serves its unique purpose and caters to specific applications. Understanding the various motor types can be overwhelming, but it’s essential for making informed decisions in your projects or business.
Whether it’s an induction motor humming quietly in a manufacturing plant or a brushless DC motor driving precision in robotics, every type has its strengths and weaknesses that make it suitable for certain tasks. Dive into this comprehensive guide as we explore the different kinds of motors and how they apply to real-world situations!
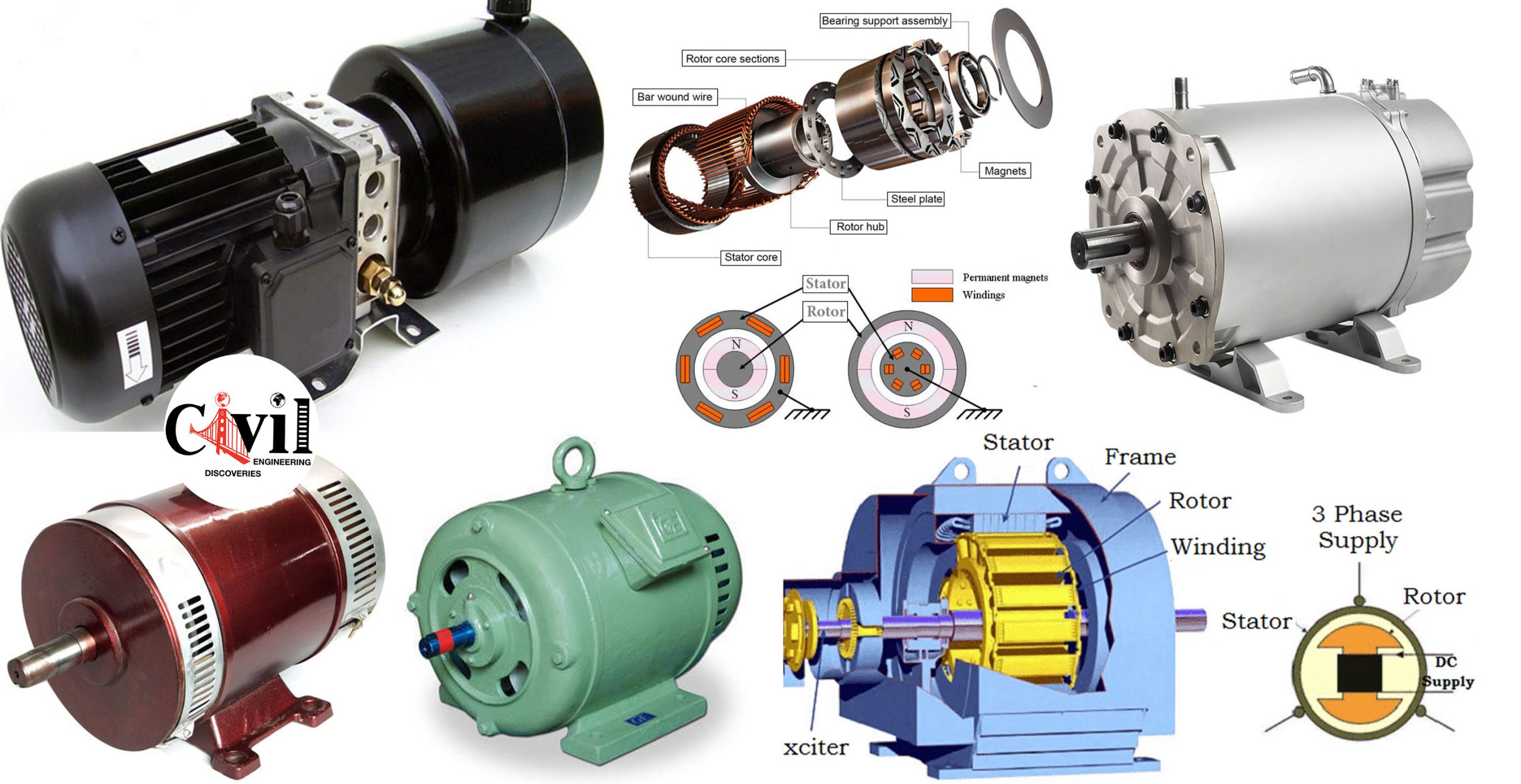
AC Motors:
AC motors are essential in various applications, transforming electrical energy into mechanical motion. They operate on alternating current and are known for their efficiency and reliability.
Induction motors dominate the industrial landscape due to their simple construction and low maintenance needs. They work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, making them suitable for heavy machinery, fans, and pumps.
Synchronous motors stand out because they maintain a constant speed regardless of load variations. This unique feature makes them ideal for applications requiring precise control, like robotics and conveyor systems.
Both types offer distinct advantages depending on specific project requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting an AC motor that best suits your application needs.
A. Induction Motors
Induction motors are a popular choice in various industrial applications due to their robustness and reliability. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where current is induced in the rotor by the stator’s magnetic field.
These motors come in two varieties: single-phase and three-phase. Single-phase induction motors are typically used for smaller appliances like fans or pumps, while three-phase models power heavy machinery.
One notable feature of induction motors is their simplicity; they have fewer components compared to other types, reducing maintenance needs. Their ability to handle overloads makes them ideal for varied operational settings.
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role as well. Many modern designs focus on minimizing energy consumption without compromising performance, aligning with global sustainability goals. This ensures that industries can reduce costs while maintaining productivity levels.
B. Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors are unique in their operation. They maintain a constant speed, no matter the load applied to them. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where precision is crucial.
These motors work synchronously with the supply current frequency. When powered, they lock onto the frequency of the electrical grid, ensuring steady performance. As a result, industries often utilize synchronous motors for tasks requiring consistent speed and torque.
Their construction typically includes rotor windings that can be magnetized by either permanent magnets or electromagnets. This flexibility allows them to adapt to various operational needs.
Applications range from large industrial machines to smaller devices within HVAC systems. Their efficiency and reliability make them popular choices across different sectors.
DC Motors:
DC motors are versatile and widely used in various applications. They convert direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy, providing precise control over speed and torque.
Brushed DC motors are one of the most common types. These motors feature brushes that conduct electricity between stationary wires and moving parts. Their simplicity makes them easy to use but requires maintenance due to wear on the brushes.
On the other hand, brushless DC motors eliminate this need for maintenance. They use electronic controllers to manage power delivery. This design enhances efficiency and extends operational life, making them ideal for high-performance applications like drones or electric vehicles.
Whether it’s powering toys or driving industrial machinery, DC motors play a crucial role across industries. Their adaptability allows engineers to select models tailored specifically to meet demanding requirements within their projects.
A. Brushed DC Motors
Brushed DC motors are a staple in various applications due to their simplicity and reliability. These motors use brushes and a commutator to provide electrical current, allowing for smooth rotation.
One of the key advantages of brushed DC motors is their straightforward design. This makes them easy to control and maintain, making them popular choices in consumer electronics like toys and small appliances.
Moreover, these motors deliver high torque at startup. This feature is particularly useful in devices requiring immediate power, such as power tools and automotive starters.
However, they do have some downsides. The brushes wear out over time, necessitating periodic replacement which can lead to increased maintenance costs.
Despite this drawback, the ease of integration into various systems keeps brushed DC motors as a preferred option across multiple industries. Their versatility continues to drive innovation in motor technology.
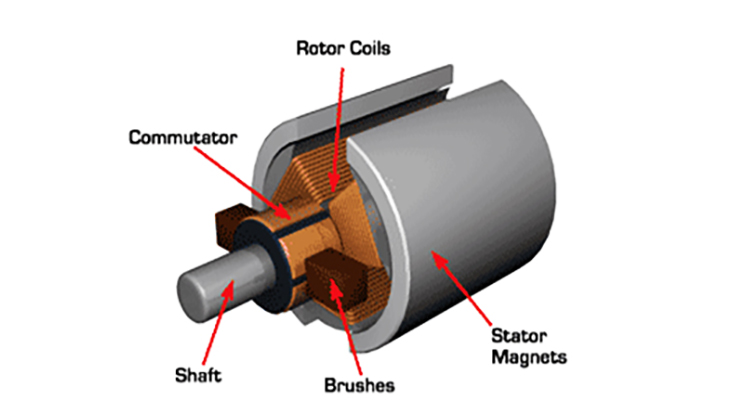
B. Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) have gained immense popularity in various applications due to their efficiency and reliability. Unlike traditional brushed motors, they eliminate the need for brushes, which reduces maintenance and enhances longevity.
These motors operate using an electronic controller that manages the commutation process. This design allows for smoother operation and higher power density. As a result, BLDC motors are quieter and generate less heat during use.
They excel in scenarios requiring precision and speed control, making them ideal for robotics, drones, and industrial automation. Their compact size also makes them suitable for consumer electronics like computer cooling fans or electric bicycles.
Moreover, brushless DC motors offer impressive torque at lower speeds while maintaining energy efficiency across different loads. The versatility of these motors continues to drive innovation across numerous industries.
Stepper Motors and their Applications
Stepper motors are unique devices that convert electrical pulses into precise mechanical movements. Unlike traditional motors, they move in discrete steps, allowing for accurate positioning and control.
These motors excel in applications requiring high precision. They’re commonly found in 3D printers, CNC machines, and robotics. Their ability to maintain position without needing feedback makes them ideal for these tasks.
In the medical field, stepper motors drive equipment like MRI machines and surgical robots where accuracy is crucial. In automation systems, they help with assembly lines by ensuring components move exactly as needed.
Another exciting application lies within consumer electronics. From cameras to scanners, stepper motors enable smooth zooming and focusing functions that enhance user experience. With versatility across various sectors, their demand continues to grow as technology advances.
Servo Motors and their Uses
Servo motors are precision devices that provide accurate control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration. This makes them ideal for applications requiring tight feedback loops and precise movements.
Commonly found in robotics, they enable smooth motion and positioning in robotic arms. Their ability to maintain exact positions is crucial for tasks like assembly and welding.
In the automotive industry, servo motors play a vital role in steering systems and automated mechanisms. They ensure responsiveness that enhances safety features.
Other uses include CNC machines where precision machining depends on reliable movement control. Additionally, servo motors are integral to camera autofocus systems, allowing rapid adjustments without compromising image quality.
The versatility of these motors extends into consumer electronics as well. Devices like drones utilize them for stabilization during flight, ensuring seamless operation even under varying conditions.
Hybrid and Linear Motors
Hybrid motors combine the features of both AC and DC technologies. They offer efficiency and versatility in various applications. This makes them ideal for electric vehicles, robotics, and industrial automation.
Linear motors are another fascinating type. Unlike traditional rotary motors, they produce linear motion directly from electrical energy. These motors excel in high-speed transport systems like maglev trains or precision positioning devices found in manufacturing.
Both hybrid and linear motors play crucial roles across industries. Their adaptability allows engineers to tailor solutions based on specific needs, whether it’s subtle movements or rapid acceleration.
The advancement of these motor types continues to push technological boundaries. As demands for efficiency rise, innovations will likely enhance their performance even further.

Choosing the Right Motor for Your Application
Selecting the right motor for your application hinges on several key factors. First, consider the type of load you will be driving. Does it require high torque or speed?
Next, evaluate the power supply available in your setup. AC and DC motors come with their unique requirements and efficiencies that can affect performance.
Think about environmental conditions as well. Will the motor need to withstand extreme temperatures or moisture? Certain motors perform better under specific conditions.
Additionally, factor in control systems used in your project. Servo motors might be ideal for precision tasks, while stepper motors excel in applications requiring accurate positioning.
Budget constraints also play a role. Assessing long-term costs versus initial investment is crucial since some options may offer savings through longevity and efficiency.
Understanding these elements helps ensure you make an informed decision tailored to meet your project’s needs effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding motor types and their applications can significantly enhance your projects, whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a hobbyist. Each type of motor—AC motors like induction and synchronous, as well as DC motors including brushed and brushless variants—offers unique advantages suited to specific tasks. Stepper motors excel in precise control, while servo motors provide excellent speed regulation.
Hybrid and linear motors present innovative solutions for specialized needs. Selecting the right motor requires careful consideration of factors such as efficiency, torque requirements, size constraints, and operational environment. By aligning these factors with the appropriate motor type, you ensure optimal performance for your application.
Navigating the world of motors doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With this knowledge at your fingertips, you’re better equipped to make informed decisions that will drive success in your projects.