Introduction to the growing popularity of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The surge in Electric Vehicle (EV) adoption is more than just a trend; it’s a revolution on wheels. As drivers embrace the eco-friendly alternatives to traditional gasoline cars, we are witnessing a significant shift towards sustainable transportation. EVs promise not only reduced carbon footprints but also lower operational costs and an exciting driving experience. With benefits spanning from environmental conservation to energy independence, it’s no wonder that electric vehicles have captured the hearts of so many.
However, as with any major transformation, challenges lie ahead. The integration of millions of EVs into our daily lives raises critical questions about our current electricity grid’s capacity and stability. How will we support this growing demand for charging infrastructure? What impact will widespread EV adoption have on our existing power supply? Join us as we explore these pressing issues while uncovering solutions that can help pave the way for a greener future.
Benefits of EVs for drivers, the environment, and energy independence
Electric Vehicles (EVs) offer a host of advantages for drivers. The most immediate benefit is savings on fuel costs. Electricity tends to be cheaper than gasoline, meaning lower monthly expenses.
Moreover, EVs require less maintenance than traditional vehicles. With fewer moving parts, there’s less that can go wrong over time. This reduces repair bills and extends the vehicle’s lifespan.
Environmental benefits are significant as well. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air in urban areas. They help combat climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions when powered by renewable energy sources.
Energy independence is another compelling reason to embrace EV technology. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, countries can strengthen their energy security and promote sustainable practices at home.
With increased adoption of electric vehicles comes an opportunity for a greener future—one where innovation leads the charge toward sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
Grid challenges associated with widespread EV adoption
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction, the strain on our power grids becomes increasingly evident. The surge in demand for charging infrastructure raises serious concerns about capacity and reliability.
Many grids were not designed to handle the sudden influx of electricity needed for mass EV charging. This shift could lead to outages during peak usage times if not managed properly.
Additionally, regional disparities complicate matters. Urban areas may face more severe challenges due to higher concentrations of EV owners compared to rural regions.
The timing of charging also poses a challenge; if everyone plugs in after work, it can overwhelm local systems. A coordinated approach is essential to prevent potential grid failures as we embrace this revolutionary mode of transportation.
Addressing these hurdles will require innovation and collaboration across multiple sectors within energy management systems.
Limited charging infrastructure and solutions being implemented
As electric vehicles gain traction, the demand for charging stations is skyrocketing. Yet, many regions still lack sufficient infrastructure to meet this need. Urban areas often see more chargers than rural ones, leaving drivers in less populated locations at a disadvantage.
To tackle this issue, innovative solutions are emerging. Governments and private sectors are partnering to expand networks of fast-charging stations along highways and in city centers. These collaborations aim to create a seamless experience for EV owners.
Moreover, technology is evolving to support home charging options. Smart chargers allow users to schedule charging during off-peak hours when electricity costs are lower.
Public awareness campaigns also play a crucial role. Educating potential buyers about available resources can ease range anxiety and encourage EV adoption even further. The push for better infrastructure is essential as we move towards an electrified future.
Impact on electricity demand and grid stability
Widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) significantly impacts electricity demand. As more drivers switch to EVs, the surge in charging needs can place considerable strain on existing grid systems.
During peak hours, this increased demand could lead to overload situations. Power plants may struggle to keep up, resulting in potential outages or reduced service reliability.
Moreover, managing this fluctuating energy consumption poses challenges for grid operators. They must balance supply and demand effectively while ensuring that infrastructure remains robust.
The timing of charging also plays a crucial role. If many users charge their cars simultaneously during evening hours, it could create spikes in usage that disrupt stability.
Monitoring these patterns will be essential as we move forward with integrating EVs into our daily lives. Adaptations will be necessary not only to meet current demands but also accommodate future growth in the EV market.
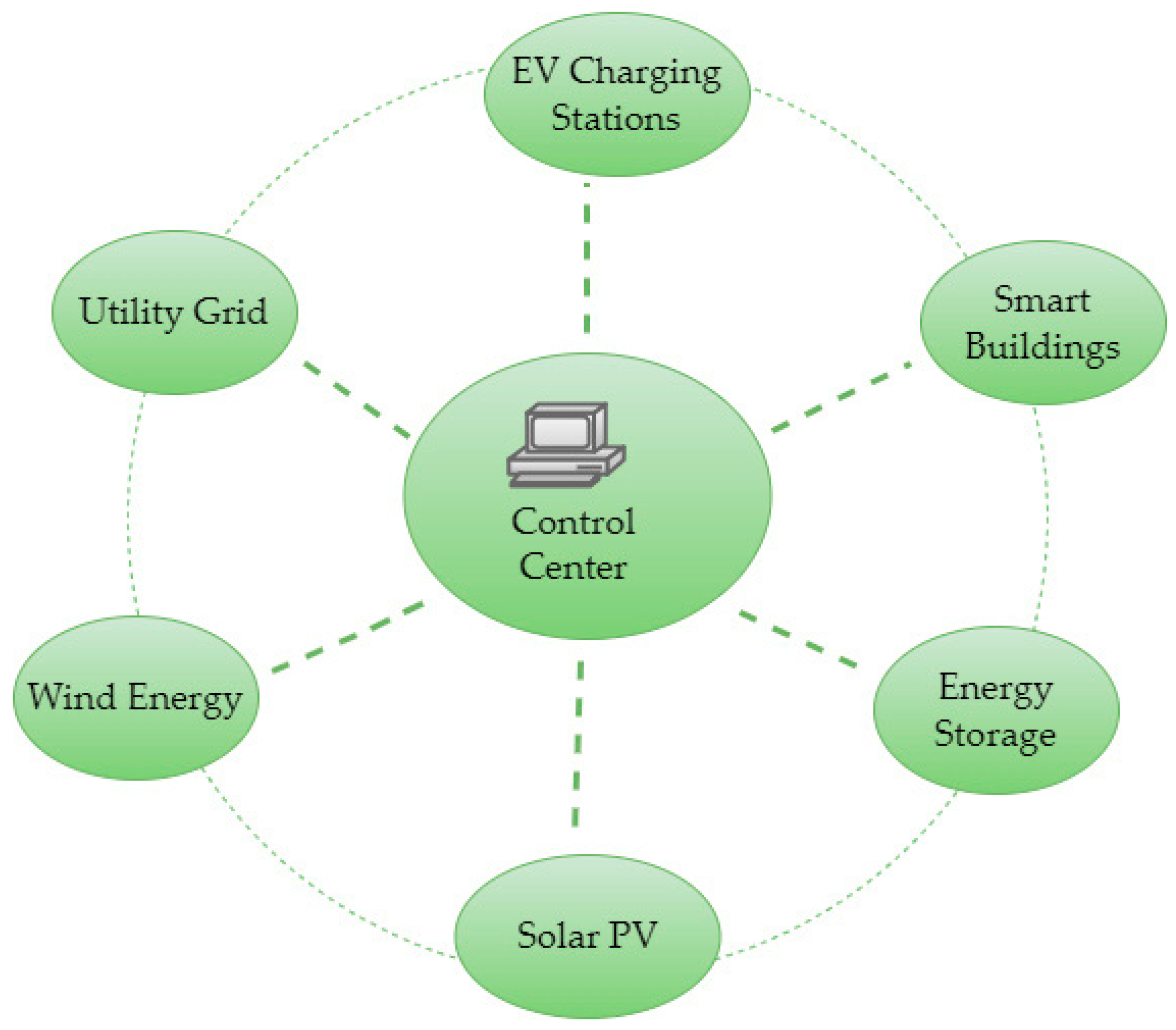
Role of renewable energy in supporting EV charging
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in the evolution of electric vehicle (EV) charging. By integrating solar, wind, and other clean sources into the grid, we can significantly reduce carbon emissions associated with electricity generation.
Solar panels on homes or charging stations provide an excellent opportunity to harness sunlight during peak driving hours. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and supports a sustainable ecosystem for EV users.
Wind energy is another powerful ally. Wind farms can generate substantial amounts of electricity that feed directly into the grid, ensuring that when demand spikes due to widespread EV usage, renewable resources are ready to step up.
Moreover, using renewable energy for EV charging promotes energy independence. It allows regions to produce their own clean power rather than relying heavily on imported oil or gas.
As technology advances, battery storage systems will further enhance this synergy by allowing excess renewable energy to be stored and used when needed.
Future outlook and potential solutions to overcome grid challenges
The future of electric vehicle (EV) adoption hinges on innovative solutions to grid challenges. As the number of EVs increases, smart grids become essential. These advanced systems can manage electricity flow more efficiently, adapting in real time to changes in demand.
Battery storage technologies also offer promising avenues. By storing excess energy generated during off-peak hours, we can mitigate stress on the grid during peak charging times. This balance is crucial for maintaining stability as more drivers transition to electric vehicles.
Moreover, incentives for home solar installations could empower individuals to charge their EVs using renewable energy sources. Such initiatives not only promote clean energy but also reduce reliance on traditional power plants.
Collaboration between governments and private sectors will be vital in expanding charging infrastructure and integrating renewable resources into the grid system effectively. Through these concerted efforts, we can pave a smoother path toward widespread EV adoption while addressing critical grid challenges head-on.
Conclusion
The rise of electric vehicles is reshaping the transportation landscape. As more drivers opt for EVs, the benefits are clear: reduced emissions, lower fuel costs, and greater energy independence. However, this widespread adoption brings significant grid challenges that need to be addressed.
Limited charging infrastructure poses a serious barrier. While initiatives are underway to expand charging stations across urban and rural areas, many locations still lack sufficient access. Innovative solutions like fast-charging networks and home-based chargers aim to bridge these gaps.
The increased electricity demand from millions of EVs can strain existing power grids. Load management strategies will be essential to maintain grid stability during peak usage times when most drivers plug in their vehicles after work or on weekends.
Renewable energy sources play a pivotal role in supporting the growing needs of EV charging. Solar and wind power can contribute significantly to reducing reliance on fossil fuels while providing clean energy for electric vehicle operations.
Looking ahead, potential solutions such as smart grids, battery storage systems, and vehicle-to-grid technology offer hope for overcoming these challenges with effective planning and collaboration among stakeholders. The future presents both obstacles and opportunities as we navigate this electrifying transition toward greener transportation choices that benefit us all.

